You are viewing Asia Pacific
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- EMENA
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Russia
- South Asia
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Global
Choose Your Location:
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
Popular Searches
- Animal Nutrition & Health
- KEMZYME™
- KEMZYME™ MAP Dry
KEMZYME™ MAP Dry Enzymes For Feed | Kemin Asia Pacific
Maximizing Energy and Amino Acid Release
Many feed ingredients are not fully digested by animals. However, by adding enzymes to feed, the digestibility of these components can be enhanced. Enzymes are now well-proven and successful catalysts that allow feed producers to extend the range of raw materials used and improve the efficiency of existing formulations. KEMZYME™ MAP Dry is a stabilized multi-enzyme formulation developed by Kemin to improve the digestibility of raw materials, increase the nutrient level and animal performance and reduce the cost of production. The formula is based on NSP enzymes, multi-amylase and multi-protease.
Unique Features of KEMZYME™ MAP Dry
- Unique combination of NSP enzymes, multi-amylase and multi-protease in order to improve the digestibility of NSPs, starch and amino acids
- Combination of multi-source enzymes to ensure activity in a wider pH range
- Synergistic actions of multiple enzymes
Enzyme Systems in KEMZYME™ MAP Dry
NSP Enzymes
- Xylanase
- Cellulase
- Beta glucanase
- Pectinase
Multi-Amylases
- α-Amylase
- Glucoamylase
- Pullulanase
Multi-Proteases
- Acid Protease
- Alkaline Protease
- Neutral Protease
NSP Multi-Enzymes
All enzyme raw materials used in the KEMZYMETM MAP Dry formulation are selected from an extensive database with over 100 enzymes which have been screened by Kemin. The NSP enzymes (xylanase, cellulase, beta glucanase and pectinase) contained in KEMZYMETM MAP Dry are specially designed to release energy from multi-substrate complex diets for animals.
Multi-Amylases
Dietary starch is a polymer made up of glucose, which is linked by two types of bonds – α 1,4 and α 1,6. Each bond is classified as “endo” and “exo” based on location in the molecule. To maximize starch digestion, both bonds have to be hydrolyzed from all sides. The multi-amylase system ( α amylase, gluco amylase and pullulanase) ensures the breakage of exo and endo bonds to achieve better starch digestibility.
Multi-Proteases
Many commercial feed enzymes use a “neutral protease” enzyme for the improvement of protein utilization in animal diets. Kemin’s patented multi-protease system (acidic, neutral and alkaline proteases) demonstrate that the combined application of acidic, neutral and alkaline proteases release more amino acids and significantly improve the bioavailability of nitrogen in vivo.
Multi-Protease Model for Animal System
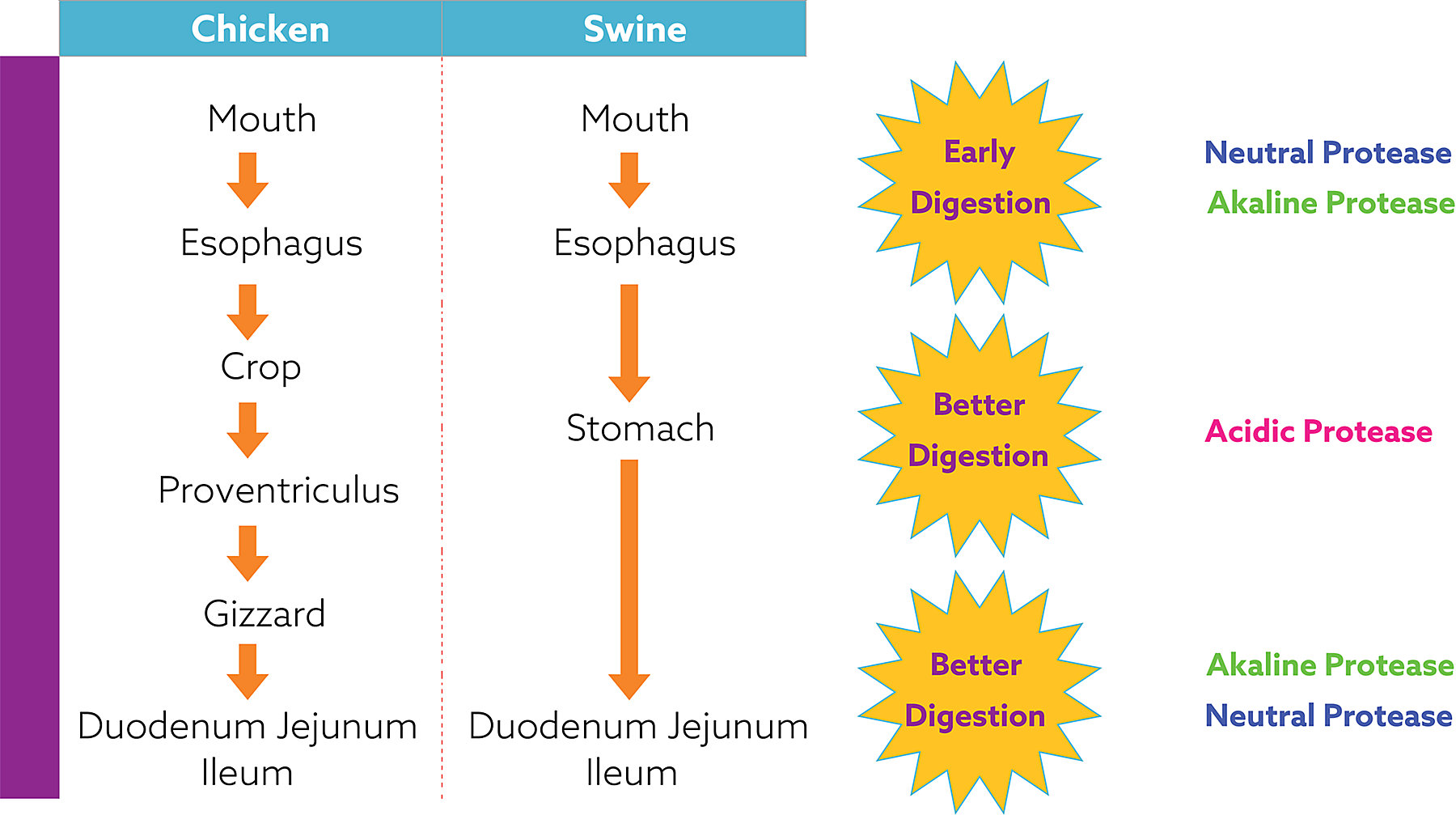
Multi-Proteases are Better Than Single Protease Enzymes
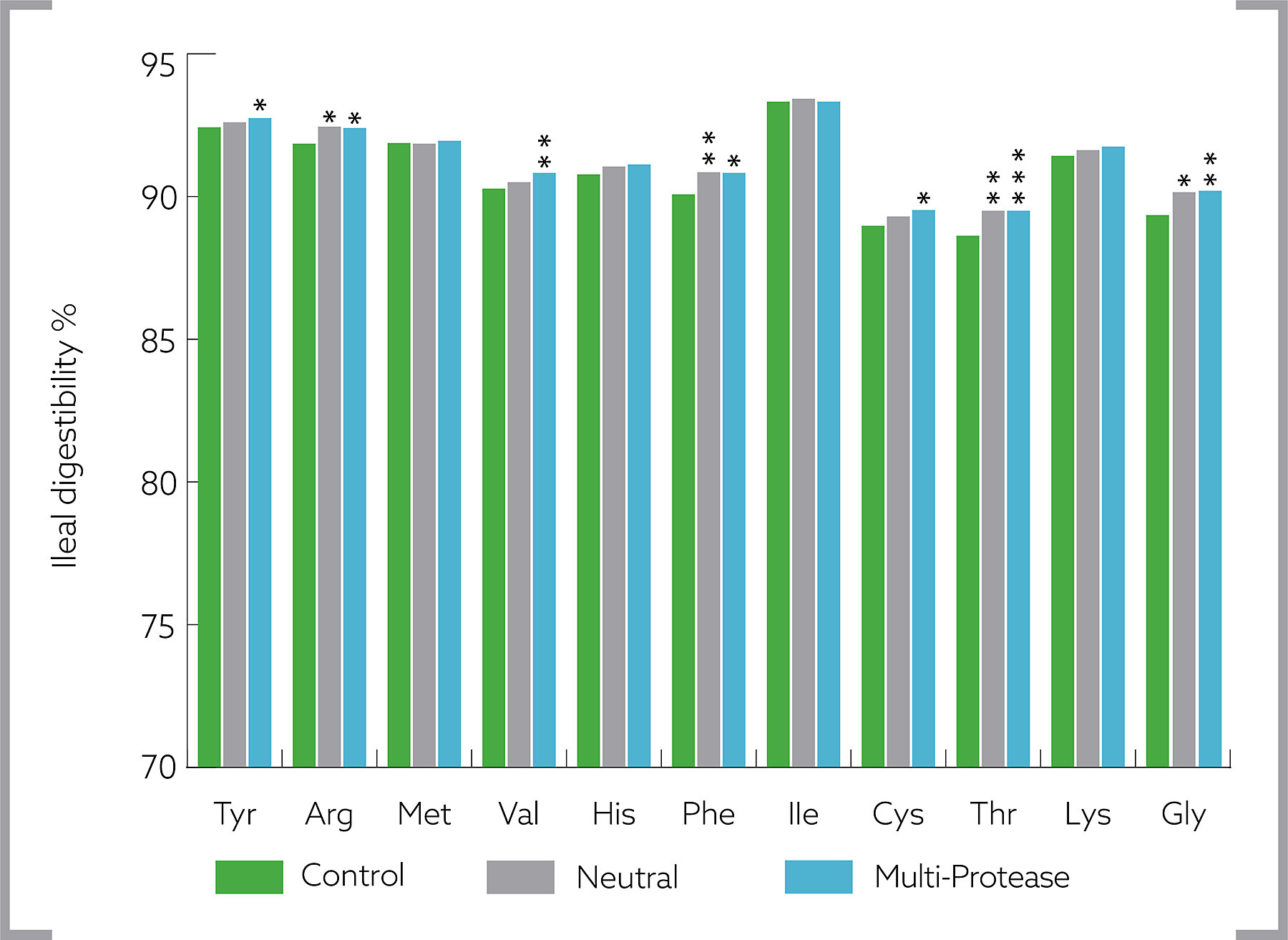
In vivo ileal digestibility studies in broilers conducted at Massey University, New Zealand, showed that multi-proteases, a combination of proteases with different pH optima, have a significant effect on amino acid digestibility of corn-soybean meal diets in broilers over a single neutral protease enzyme. Multi-enzyme products containing a multi-protease system will therefore achieve higher economic benefit through the energy and amino acid sparing effects on the animal diets.
Efficacy of KEMZYME™ MAP Dry
Commercial Broilers
A growth trial was conducted at Bangkok Animal Research Center, Thailand. 240 birds were divided in to 3 groups with 8 replicates and 10 birds per replicate. Diets used for the growth trial were (1) Positive control diet (corn-soybean), (2) Negative control diet (energy reduced by 100 kcal/kg by replacing corn and soybean using DDGS, canola meal, cassava, rice bran and crude protein reduced by 0.5%) and (3) Negative control diet + KEMZYMETM MAP Dry (0.5 kg/t). Results are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Effect of KEMZYME™ MAP Dry on the growth performance of commercial broilers Positive Control Diet Negative Control Diet Control + KEMZYME™
| Positive Control Diet | Negative Control Diet | Control + KEMZYME™ MAP DRY | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight Gain | 2930ₐ | 2681ₐ | 2800ₐ |
| Feed Intake (g) | 5002ₐ | 4993ₐ | 5048ₐ |
| Feed Conversion Rate | 1.71ₐ | 1.84 | 1.80ₐ |
Commercial Layers
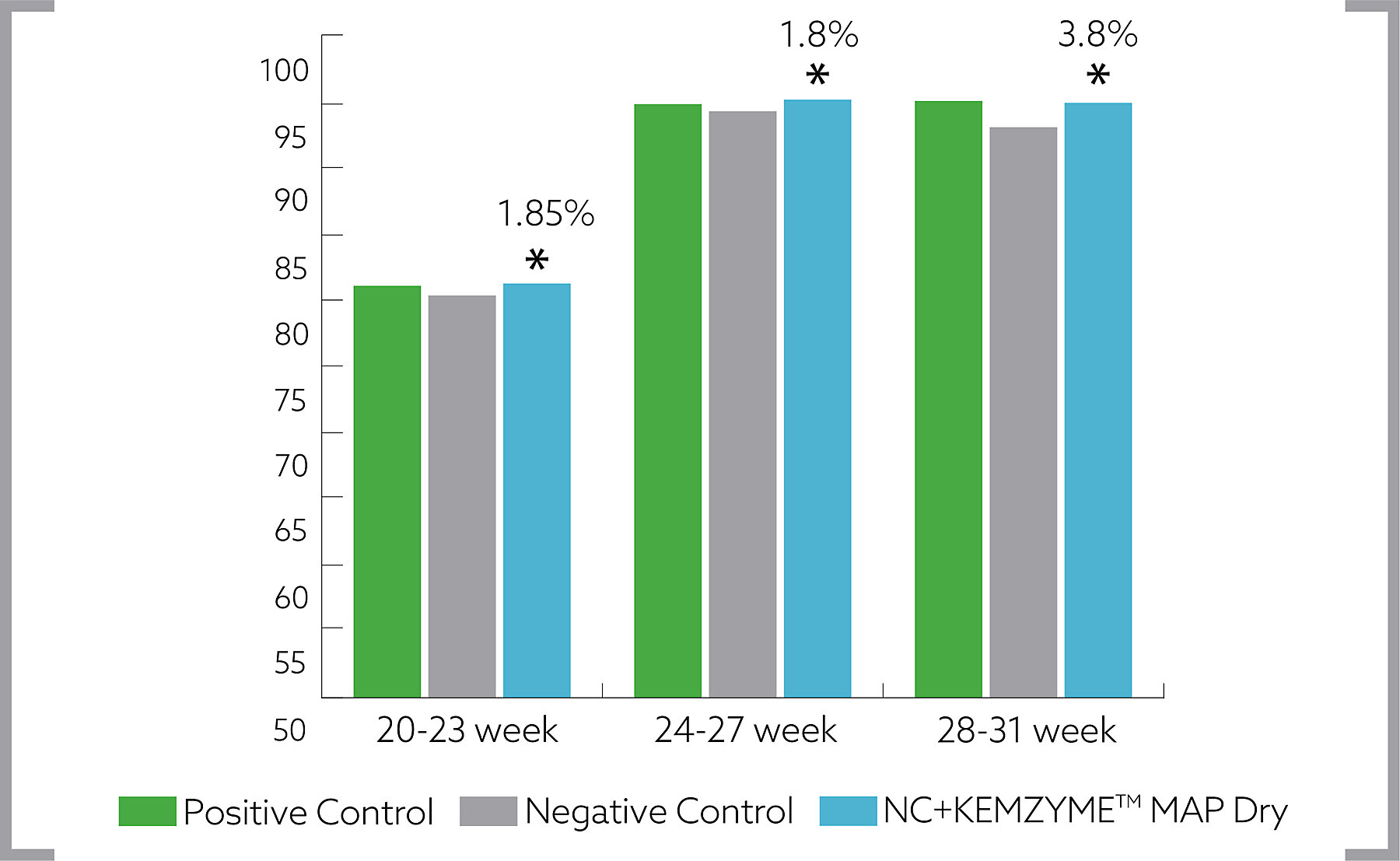
A study was conducted at CNF Farm in Kabinburi, Thailand, at a closed monitor layer house with wire laying cages in air-step arrangements. The birds were kept 2 per cage with 6 replicate and 20 birds per replicate. Diets used for the trial were (1) Positive control diet (corn, soybean, meat cum bone meal), (2) Negative control diet (energy reduced by 60 kcal/kg by replacing corn and soybean using DDGS, cassava, rice bran and crude protein reduced by 0.5%) and (3) Negative control diet + KEMZYME™ MAP Dry (0.25 kg/t).
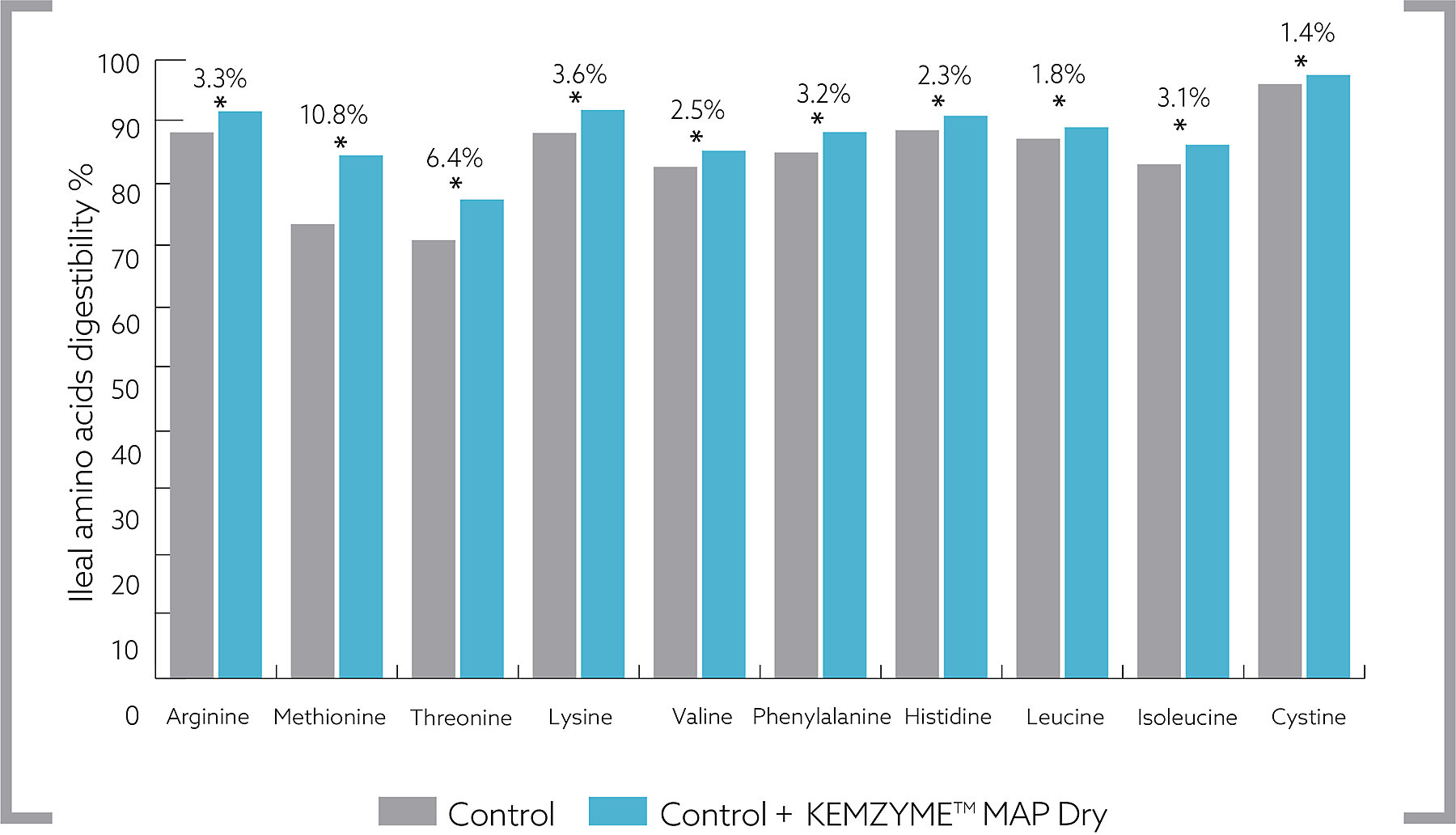
Improving Ileal Amino Acid Digestibility in Swine
A swine trial was conducted at the Institute of Agricultural Studies, Vietnam to determine KEMZYME™ MAP Dry’s conclusive performance on digestibility. Pigs were housed individually in metabolism crates (0.8 x 1.5 m). Each metabolism crate had a collection tray for urine collection and a fine-mesh net just above the tray for fecal collection allowing for separate but total collection of feces and urine. Pigs were fed ad libitum and diets were fed in mash form. Results of the ileal amino acid digestibility trial are shown in figure 3.
Growth Performance of Pigs
The swine growth trial was conducted from 30 to 90 days period at Institute of Agricultural Studies (IAS) Vietnam. Diets used for the growth trial were (1) Positive control diet (corn, soybean, rice bran, fish meal), (2) Negative control diet (Less 60 kcal/kg ME and 0.5% Crude Protein), (3) Negative control diet + KEMZYMETM MAP Dry (0.5 kg/t) and (4) Negative control diet + Competitor enzyme product (0.5 kg/t). Results of the performance trial are shown in table 2.
| Positive Control Diet | Negative Control Diet | Control + KEMZYME™ MAP DRY | Control + Competitor Enzyme | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight Gain (kg/pig) | 25.95ₐ | 25.12ₐ | 27.66ₐ | 25.90a |
| Feed Intake (g) | 49.08ₐ | 49.22ₐ | 49.63ₐ | 48.78 |
| Feed Conversion Rate | 1.89ₐ | 1.96c | 1.79ₐ | 1.88a |
Benefits of KEMZYME™ MAP Dry
- A multi-enzyme system for multi-substrate complex diets
- Accommodates many different kinds of raw materials in feed formulation
- Ensures better starch/protein/NSP digestion
- Reduces feed cost
Mixing Ratio
- On top application: 250 g per ton
- Feed reformulation: 500 g per ton
Please contact a Kemin representative for more details.
Presentation
25 Kg paper craft bag
Storage
Store in a cool, dry place and away from sunlight.
Have a question about KEMZYME™ MAP Dry?
- California Supply Chain Act
- Email Disclaimer
- GDPR Personal Data Addendum
- General Terms & Conditions for Vendors
- Global Environmental Policy Statement
- Indirect Cost Estimates
- Kemin Terms & Conditions
- Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement
- Privacy Policy
- Sitemap
- Change Cookie Consent
- Animal Welfare Statement
© Kemin Industries, Inc. and its group of companies All rights reserved. ® ™ Trademarks of Kemin Industries, Inc., USA
Certain statements may not be applicable in all geographical regions. Product labeling and associated claims may differ based upon government requirements.
Thank you for visiting Kemin.com.
Your questions and feedback are important to us. Let us know how we can help you learn more about Kemin, our products, our services or our website.
Interested in starting a career with Kemin?
